Australian Financial Services Compliance Simplified
Mar 10, 2025
Our comprehensive guide on Australian financial services compliance and compliance management software offers a detailed look at the compliance requirements that financial services companies in Australia need to adhere to. We delve into the regulations and guidelines set forth by key regulatory bodies such as the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC), the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA), and other pertinent legislation.
Whether you are a seasoned professional in the financial services sector or new to the industry, our guide is a must-have resource to ensure compliance and stay ahead in the dynamic landscape of Australian financial regulations.
Confused by AFS license requirements or ASIC audits? Get a free 30-minute consultation with our financial compliance expert.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape of Australian Financial Services
The Australian financial system is governed by a complex network of regulatory authorities, each with its own mandate and responsibilities. To ensure compliance and protect the interests of consumers, it is crucial for financial services providers to understand the roles and requirements of these key regulators.
Key Regulatory Authorities
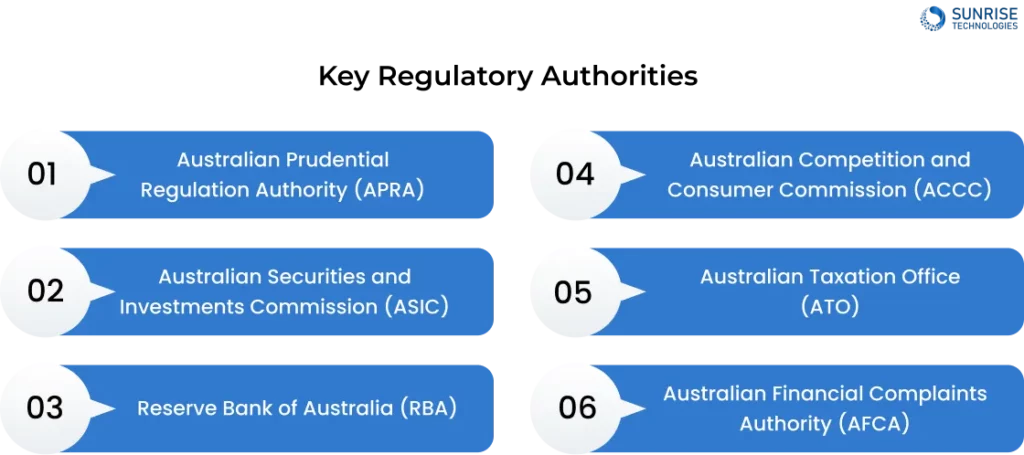
- Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA): APRA is the primary regulator responsible for licensing and overseeing banking, insurance, and superannuation entities. It sets prudential standards and provides guidance on capital adequacy, liquidity, and risk management to safeguard the interests of depositors, insurance policyholders, and superannuation fund members.
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC): ASIC is the consumer protection and market integrity regulator. It oversees financial markets, intermediaries, products, services, and corporate governance to ensure the efficiency and development of the economy while reducing business costs.
- Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA): The RBA is the central bank responsible for managing the nation's currency and monetary policy. It sets the official cash rate, which influences the cost of borrowing and affects the availability of credit. The RBA also sets prudential standards for financial institutions and provides guidance on financial stability.
- Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC): The ACCC promotes competition and prevents anti-competitive behavior in the financial system. It ensures that financial products and services are offered in a fair and transparent manner, protecting consumers from misleading practices.
- Australian Taxation Office (ATO): The ATO administers the Australian taxation system, ensuring that individuals and businesses comply with their taxation obligations and that the revenue collected is used to fund public services.
- Australian Financial Complaints Authority (AFCA): AFCA is an independent dispute resolution service that provides a free, fast, and fair resolution process for consumers and small businesses with disputes against their financial service providers.
Regulatory Responsibilities
- ASIC: ASIC is responsible for licensing and monitoring financial services providers, assessing compliance with legal obligations to operate fair and transparent markets, supervising and enforcing disclosure requirements to retail investors, and administering company fundraising through the issue or sale of financial products.
- APRA: APRA is responsible for licensing and regulating entities engaging in consumer credit activities, assessing the prudential soundness of banks and other ADIs, monitoring the activities of the banking, insurance, and superannuation industries, and supervising superannuation trustees and funds.
- RBA: The RBA is responsible for setting the official cash rate, conducting open market operations, issuing currency, overseeing the clearing and settlement of payments, and promoting the safety and efficiency of the payments system.
Key Legislation and Regulations
Financial services providers in Australia must adhere to a range of legislation and regulations, including:
1. Corporations Act 2001: The Foundation of Company Governance
The Corporations Act 2001 is a cornerstone of Australian corporate law, providing the legal framework for the formation, operation, and governance of companies, including those in the financial services sector. This Act sets out the rules and regulations that companies must follow to ensure transparency, accountability, and fair dealing.
Key provisions of the Corporations Act 2001 include:
- Company formation and registration.
- Share capital and shareholding structures.
- Directors' duties and responsibilities.
- Financial reporting and disclosure requirements.
- Corporate governance and accountability.
2. Australian Securities and Investments Commission Act 2001: Empowering ASIC
The Australian Securities and Investments Commission Act 2001 establishes ASIC as the primary regulator of financial services in Australia. This Act outlines ASIC’s powers and functions, including:
- Licensing and regulating financial services providers.
- Monitoring and enforcing compliance with financial services laws.
- Investigating and prosecuting breaches of financial services laws.
- Providing guidance and education to financial services providers and consumers.
3. National Consumer Credit Protection Act 2009: Safeguarding Consumer Credit
The National Consumer Credit Protection Act 2009 regulates the provision of consumer credit, including credit cards, personal loans, and home loans. This Act aims to protect consumers by ensuring that credit providers lend responsibly and transparently.
Key provisions of the National Consumer Credit Protection Act 2009 include:
- Responsible lending obligations.
- Credit licensing and registration.
- Disclosure requirements for credit contracts.
- Debt collection and hardship provisions.
4. Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing Act 2006: Combating Financial Crime
The Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing Act 2006 requires financial services providers to implement measures to detect and prevent money laundering and terrorism financing. This Act aims to protect the Australian financial system from the risks of financial crime.
Key provisions of the Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing Act 2006 include:
- Customer due diligence and verification.
- Reporting of suspicious transactions.
- Ongoing monitoring of customer activity.
- Implementation of anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing programs.
5. Privacy Act 1988: Protecting Personal Information
The Privacy Act 1988 sets out the requirements for the collection, use, and storage of personal information by financial services providers. This Act aims to protect the privacy of individuals by ensuring that their personal information is handled in a fair, transparent, and secure manner.
Key provisions of the Privacy Act 1988 include:
- Collection and disclosure of personal information.
- Use and disclosure of personal information.
- Data quality and security.
- Access to and correction of personal information.
Compliance Strategies and Best Practices
To ensure compliance with the regulatory framework, financial services providers should implement the following strategies and best practices:
- 1. Develop and maintain a comprehensive compliance program: This should include policies, procedures, and controls that address all relevant regulatory requirements.
- 2. Provide regular training and education for employees: Ensure that all staff members are aware of their compliance obligations and understand the importance of adhering to regulations.
- 3. Conduct regular risk assessments: Identify and assess the risks associated with your business activities and implement appropriate risk management strategies.
- 4. Implement robust internal controls: Put in place effective controls to prevent, detect, and mitigate compliance breaches.
- 5. Engage with regulators: Maintain open and transparent communication with regulatory authorities and be proactive in addressing any concerns or issues that arise.
Stay audit-ready with our simplified checklist for AFS license holders. Perfect for financial planners, fintechs, and fund managers.

The Importance of Compliance
Compliance with the regulatory framework is essential for financial services providers in Australia. It helps to:
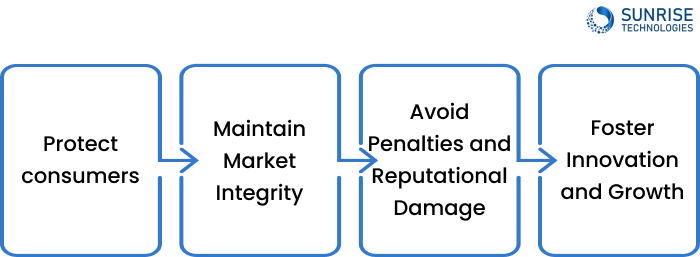
- 1. Protect consumers: Compliance ensures that financial products and services are offered in a fair, transparent, and responsible manner, safeguarding the interests of consumers.
- 2. Maintain market integrity: Compliance helps to maintain the integrity and stability of the financial system, promoting confidence and trust among investors and the general public.
- 3. Avoid penalties and reputational damage: Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, including fines and legal action, as well as reputational damage that can be difficult to recover from.
- 4. Foster innovation and growth: A well-regulated financial services industry provides a stable and supportive environment for innovation and growth, enabling firms to develop new products and services that meet the evolving needs of consumers.
Benefits of Using our Compliance Management Software
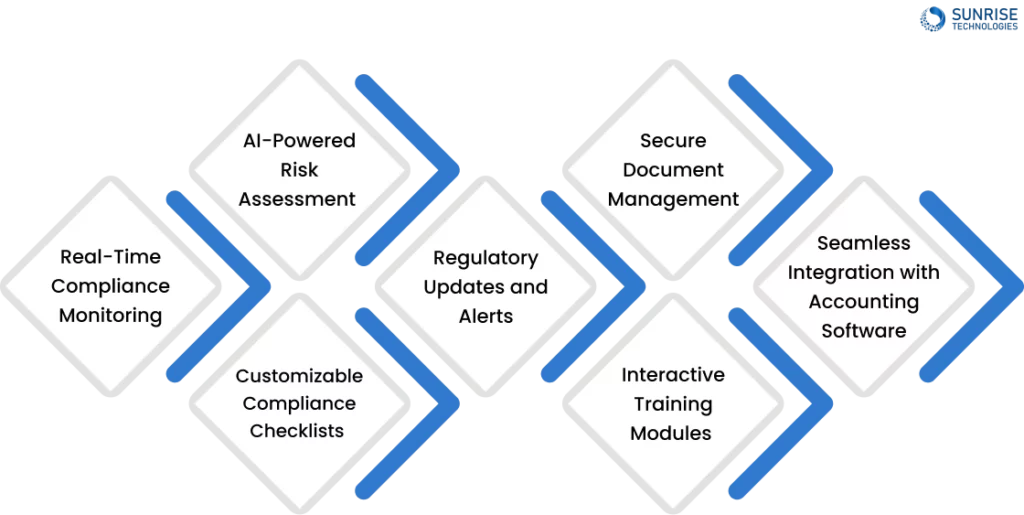
Real-Time Compliance Monitoring
Our financial compliance software real-time compliance monitoring feature provides instant visibility into your organization’s compliance status. Receive alerts and notifications for any compliance breaches or upcoming deadlines, allowing you to take proactive action and mitigate risks promptly.
AI-Powered Risk Assessment
Utilizing artificial intelligence, compliance management software offers an AI-powered risk assessment tool that analyzes data to identify potential compliance risks and trends. This proactive approach enables you to address risks before they escalate, enhancing your organization’s risk management capabilities.
Customizable Compliance Checklists
Tailor compliance checklists to suit your organization’s specific requirements with financial risk management software customizable checklist feature. Create, edit, and assign checklists to team members, ensuring that all compliance tasks are clearly defined and tracked for efficient management.
From license obligations to breach reporting—get answers fast. Chat now with a certified compliance advisor.
Regulatory Updates and Alerts
Stay informed about the latest regulatory changes and updates relevant to your industry with compliance management software regulatory updates and alerts feature. Receive real-time notifications about new regulations, ensuring that your compliance practices remain up-to-date and aligned with current requirements.
Secure Document Management
The financial risk management software secure document management feature allows you to store, organize, and share compliance-related documents with ease. Implement access controls, version tracking, and encryption to safeguard sensitive information and streamline document collaboration within your organization.
Interactive Training Modules
Enhance your team’s compliance knowledge and skills with compliance management software interactive training modules. Access a library of engaging and informative training materials on various compliance topics, empowering your team to stay informed and compliant with regulatory standards.
Seamless Integration with Accounting Software
Financial risk management software offers seamless integration with popular accounting software, enabling smooth data transfer and synchronization between platforms. This integration streamlines financial reporting processes, enhances data accuracy, and improves overall efficiency in managing financial compliance tasks.
By incorporating these advanced features, compliance management software provides Australian businesses with a comprehensive and innovative solution for managing financial compliance effectively and efficiently.
Commitment to compliance not only protects businesses and clients but also contributes to a stable and trust worthy financial services sector in Australia. By prioritizing compliance, businesses can build a strong foundation for growth, innovation, and long-term success in an increasingly complex regulatory environment.
Sam is a chartered professional engineer with over 15 years of extensive experience in the software technology space. Over the years, Sam has held the position of Chief Technology Consultant for tech companies both in Australia and abroad before establishing his own software consulting firm in Sydney, Australia. In his current role, he manages a large team of developers and engineers across Australia and internationally, dedicated to delivering the best in software technology.
Many AI prototypes fail because they overlook AFSL compliance from the start. They often lack proper audit trails, data governance, and model transparency, which are essential for meeting ASIC’s strict requirements. At Sunrise Technologies, we design AI systems that are compliant by design — ensuring your financial tools align with the Australian Financial Services Licence (AFSL) framework, from data handling to decision-making logic.
Yes. Custom software can be designed to automatically enforce compliance rules, monitor transactions, generate audit reports, and securely manage sensitive data—helping Australian financial firms meet strict regulatory requirements efficiently and reduce the risk of penalties.
Absolutely. Automation tools can generate detailed logs and reports for every action, supporting audit trails and compliance. Sunrise Technologies designs AI automation systems with built-in traceability features tailored to Australian regulatory standards in industries like healthcare, finance, and construction.
SaaS platforms must comply with the Australian Privacy Act 1988 and Australian Privacy Principles (APPs). If handling sensitive or financial data, additional standards like ISO 27001 or PCI DSS may apply. Sunrise Technologies builds platforms with compliance, encryption, and secure data storage from day one.
Yes. The Australian R and D Tax Incentive offers refunds or tax offsets for eligible software innovation and development. Sunrise Technologies can guide your technical documentation and architecture planning to align with R and D criteria and help you maximize returns.
Automation can introduce risks if not properly aligned with Australian financial regulations like ASIC and APRA standards. However, when built with compliance in mind—such as secure audit trails, data protection protocols, and regular system checks—automation actually enhances regulatory adherence. At Sunrise Technologies, we build automation solutions that meet both performance and compliance requirements.
SaaS platforms must comply with the Australian Privacy Act 1988 and Australian Privacy Principles (APPs). If handling sensitive or financial data, additional standards like ISO 27001 or PCI DSS may apply. Sunrise Technologies builds platforms with compliance, encryption, and secure data storage from day one.








Cloud Based Project Management Platform
Read the challenges we faced and how we helped
View Case Study