Benefits of using Governance, Risk, Compliance (GRC) Software
Mar 06, 2025
In today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving business landscape, effective Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) management is crucial for ensuring the integrity, resilience, and long-term success of your organization. This comprehensive guide is designed to provide business leaders, risk managers, and compliance officers with a thorough understanding of GRC software, its applications, and its benefits.
Inside this authoritative guide, you’ll discover:
What is Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC)?
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is a way for businesses to manage important parts of their operations. It helps them make good decisions, avoid problems, and follow the rules.
Governance
Governance is about how a company is run. It includes things like having clear goals, making good choices, and being responsible. Good governance helps a business stay on track and achieve its aims.
Risk
Risk is anything that could cause trouble for a company. It could be a natural disaster, a cyber-attack, or a change in the law. Risk management is about identifying risks, figuring out how likely they are to happen, and making plans to deal with them if they do.
Compliance
Compliance means following the rules and regulations that apply to a business. Every industry has its own rules, and companies need to make sure they follow them. This could include things like data protection laws, health and safety standards, or financial regulations.
GRC brings all these things together. It helps businesses manage their risks, follow the rules, and make good decisions. By having a clear GRC strategy, companies can reduce problems, save money, and build trust with customers and partners.
GRC is important for businesses of all sizes, in all industries. It helps them stay safe, stay legal, and stay successful in the long run.
See how GRC software can streamline audits, risk assessments, and compliance in real time. Book a FREE demo tailored to your industry.

What key components contribute to the success of a GRC program?
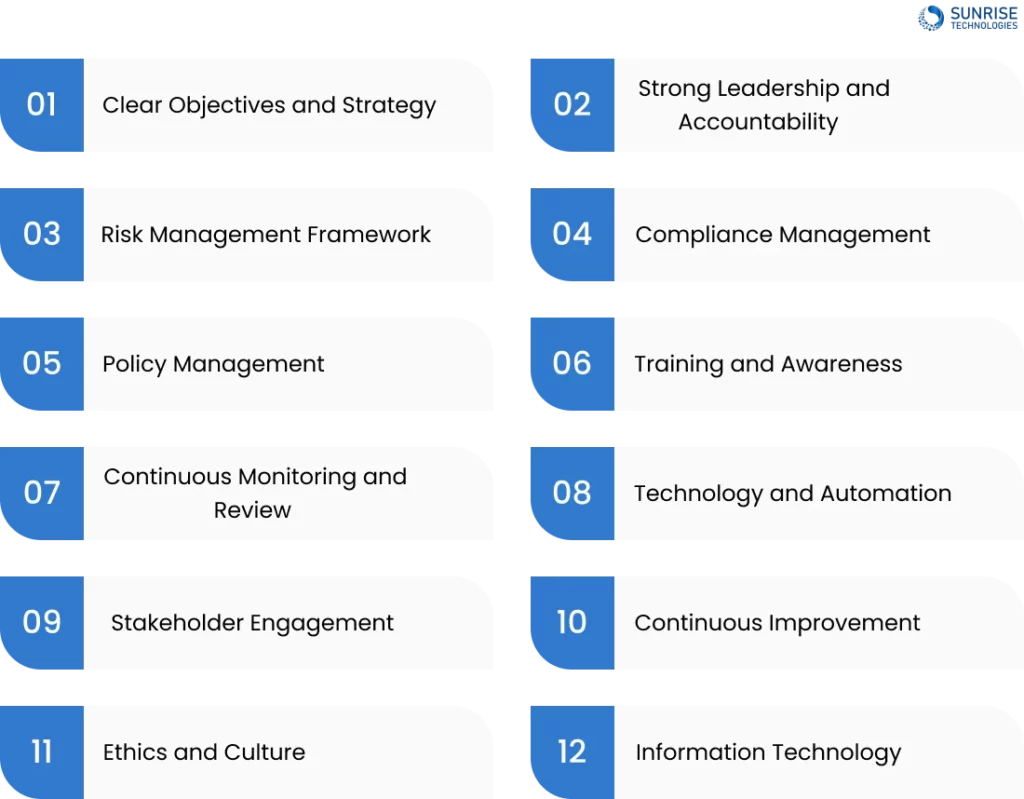
1. Clear Objectives and Strategy
A well-defined GRC strategy aligned with the organization’s overall goals and objectives ensures focus on critical areas and a unified approach. This involves setting clear objectives, defining key performance indicators (KPIs), and establishing a roadmap for GRC implementation.
2. Strong Leadership and Accountability
Active involvement and commitment from top-level management are crucial for a successful GRC program. This includes designating a GRC leader, establishing clear roles and responsibilities, and ensuring GRC is integrated into decision-making processes.
3. Risk Management Framework
A structured risk management framework helps identify, assess, and mitigate risks. This involves risk assessments, risk registers, and risk mitigation strategies to minimize potential impacts and maximize opportunities.
4. Compliance Management
Effective compliance management involves identifying, assessing, and managing compliance requirements. This includes compliance monitoring, reporting, and training to ensure adherence to regulations and standards.
5. Policy Management
A centralized policy management system ensures policies are up to date, communicated, and adhered to. This involves policy development, review, and approval processes, and training and awareness programs.
6. Training and Awareness
Regular training and awareness programs educate employees on GRC policies, procedures, and best practices. This helps to foster a culture of compliance and risk awareness throughout the organization.
7. Continuous Monitoring and Review
Regular review and assessment of the GRC program ensure it remains effective and relevant. This involves monitoring KPIs, conducting audits and assessments, and identifying areas for improvement.
8. Technology and Automation
Leveraging technology can automate GRC processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. This includes implementing GRC software, integrating with existing systems, and utilizing data analytics.
9. Stakeholder Engagement
Effective communication and engagement with stakeholders, including employees, customers, and regulators, ensure transparency and trust. This involves regular reporting, feedback mechanisms, and stakeholder surveys.
10. Continuous Improvement
A culture of continuous improvement involves learning from mistakes, identifying opportunities for improvement, and implementing changes as needed. This ensures the GRC program remains effective and aligned with the organization’s evolving needs.
11. Ethics and Culture
Promoting ethical behavior and a strong risk culture is essential for an effective GRC program. This includes setting the tone from the top, fostering open communication, and encouraging employees to speak up about concerns.
12. Information Technology
Leveraging information technology is crucial for managing GRC processes effectively. This involves implementing secure systems, managing data and information, and ensuring the reliability and availability of critical systems.
Essential Features to Consider When Selecting GRC Software
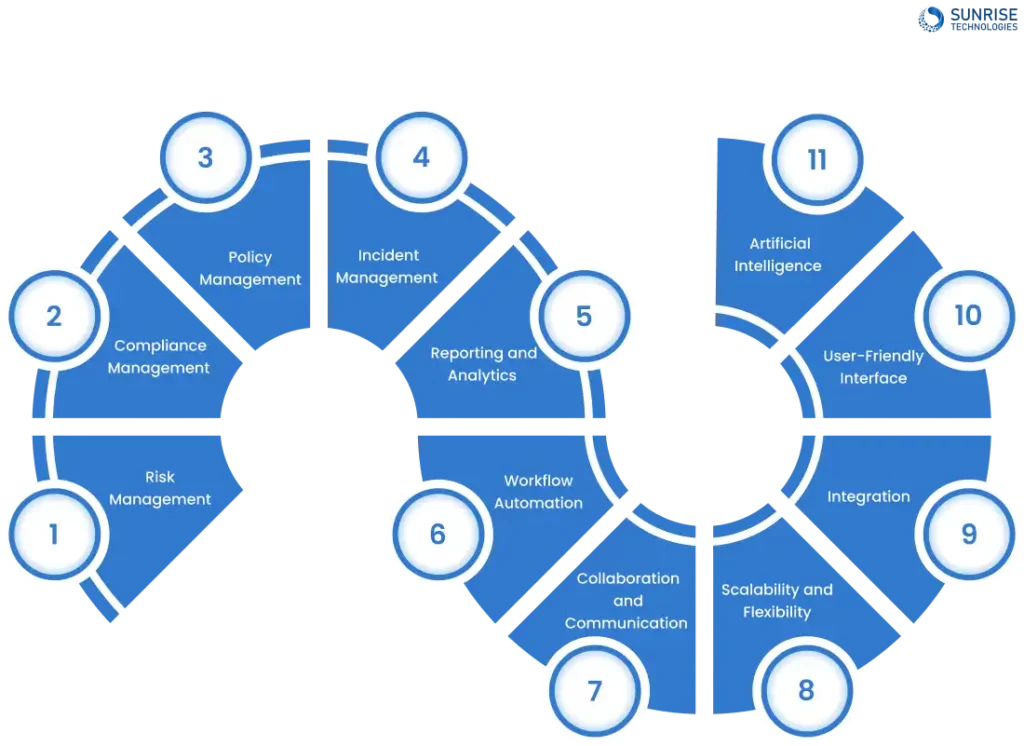
1. Risk Management
Effective GRC software should offer tools for identifying, assessing, and managing risks. It should allow you to create risk profiles, conduct risk assessments, and develop mitigation plans. The software should provide a comprehensive view of risks across the organization and help prioritize actions to address them effectively.
2. Compliance Management
Look for software that simplifies compliance management by providing features for tracking regulatory requirements, managing compliance tasks, and generating compliance reports. It should offer alerts for upcoming deadlines, automate compliance checks, and ensure adherence to relevant laws and standards.
3. Policy Management
A robust policy management module should enable easy creation, distribution, and tracking of policies and procedures. It should allow for version control, approvals, and acknowledgments to ensure that employees are aware of and compliant with organizational policies.
4. Incident Management
The software should include incident tracking and management capabilities to record, investigate, and resolve incidents effectively. It should streamline incident reporting, escalation processes, and corrective actions to minimize the impact of incidents on the business.
5. Reporting and Analytics
Comprehensive reporting and analytics features are essential for monitoring GRC performance. The software should offer customizable reports, dashboards, and data visualization tools to help you track key metrics, identify trends, and make informed decisions based on real-time data.
6. Workflow Automation
Automation of GRC workflows can streamline processes, reduce manual errors, and improve efficiency. Look for software that allows you to automate routine tasks, approvals, notifications, and escalations, freeing up time for more strategic activities and ensuring consistency in GRC processes.
7. Collaboration and Communication
Effective GRC software should facilitate collaboration and communication among stakeholders. It should provide tools for sharing information, assigning tasks, and tracking progress on GRC initiatives. Features like discussion forums, document sharing, and real-time messaging can enhance teamwork and transparency.
8. Scalability and Flexibility
Scalable GRC software should accommodate the growth and changing needs of your organization. It should offer customization options, flexible configurations, and scalability to support new users, processes, and requirements as your business evolves.
9. Integration
Seamless integration with other systems is crucial for a holistic GRC approach. Look for software that can integrate with existing tools, such as ERP systems, CRM platforms, or third-party applications, to ensure data consistency, streamline processes, and avoid duplication of efforts.
10. User-Friendly Interface
An intuitive user interface is key for user adoption and productivity. The software should be easy to navigate, with clear menus, intuitive workflows, and user-friendly features. Training requirements should be minimal, and users should be able to access information and perform tasks efficiently.
11. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence capabilities in GRC software can enhance risk prediction, automate compliance monitoring, and improve decision-making processes. AI algorithms can analyze large datasets, detect patterns, and provide insights to help organizations proactively manage risks and compliance requirements.
Navigating the GRC Software Landscape: Understanding the Different Types of Vendors
The Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) software market is vast and diverse, with numerous providers offering a wide range of solutions. To make an informed decision when selecting a GRC software vendor, it’s crucial to understand the three main categories of GRC software providers.
Legacy Software Providers
Legacy software providers typically offer solutions that were built 8 or more years ago. These providers often have the following characteristics:
- On-premises or single-code base solutions.
- Complex systems that require extensive customization, leading to long deployment times and increased costs.
- Resistance to change, which can lead to employee reluctance to use the system and the need for extensive training.
- High investment with limited return on investment due to rigid use cases and deployment difficulties.
Industry Specialized Providers
Industry specialized providers focus on specific industries, offering solutions tailored to the unique needs of those sectors. While these providers can benefit organizations within their area of specialization, they may lack flexibility outside their niche. Some key characteristics of industry specialized providers include:
- Niche focus on specific industries.
- Integration challenges when managing risks and compliance across multiple industries, potentially leading to data silos and inefficiencies.
- Limited scalability as organizations grow or diversify, potentially requiring additional GRC tools.
Point Solutions
Point solutions are designed to address a single pain point or use case for customers. While these solutions excel in their respective areas, using multiple point solutions can create fragmentation in an organization’s GRC landscape, making it difficult to have a holistic view of risk and compliance. Some key characteristics of point solutions include:
- Fragmentation in the GRC landscape due to the focus on specific needs, such as AML/KYC, business continuity management, compliance training, or threat intelligence.
- Integration complexity when trying to connect multiple point solutions, which can be costly and require investment in middleware or custom development.
- Lack of comprehensive reporting that covers all aspects of governance, risk, and compliance, making it challenging to provide stakeholders with a unified view of the organization's risk posture.
As the GRC software market continues to evolve, buyers are increasingly shifting away from point solutions and towards more integrated, comprehensive GRC platforms that can provide a holistic view of risk and compliance across the organization.
Want a deeper look at ROI, automation, and regulatory readiness? Download our comprehensive GRC guide and see why top enterprises trust automation.
Limitations of Traditional GRC Software Solutions
While traditional GRC software has been around for years, it often comes with its own set of challenges that organizations need to be aware of. Here are some of the main issues that companies face when using traditional GRC software:
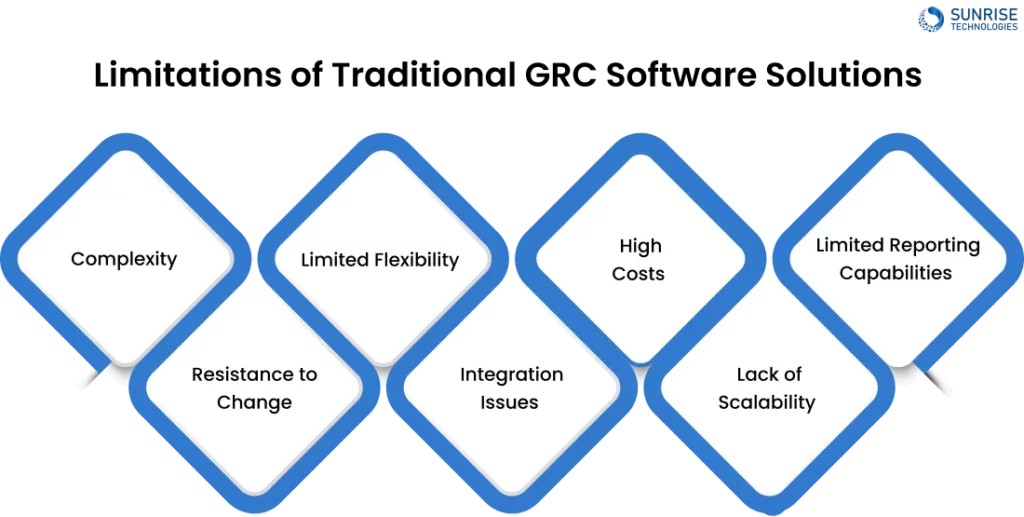
1. Complexity
Many traditional GRC software solutions are complex and require extensive customization to fit an organization’s specific needs. This can lead to long deployment times, increased costs, and challenges in adapting to regulatory changes or internal process updates.
2. Resistance to Change
Employees may resist using complex GRC software, especially if they are used to more user-friendly tools. This can lead to low adoption rates across the organization and the need for extensive training to get everyone up to speed.
3. Limited Flexibility
Traditional GRC software is often rigid and lacks the flexibility to adapt to changing business needs. As organizations grow and evolve, they may find that their GRC software is no longer able to keep up with their requirements.
4. Integration Issues
Many traditional GRC software solutions are not designed to integrate with other systems, which can lead to data silos and inefficiencies. This can make it difficult to get a complete picture of an organization’s risk and compliance landscape.
5. High Costs
Implementing and maintaining traditional GRC software can be expensive, with high upfront costs and ongoing maintenance fees. This can make it difficult for smaller organizations to justify the investment.
6. Lack of Scalability
As organizations grow and expand, their GRC needs often change. Traditional GRC software may not be able to scale to meet these changing requirements, leading to the need for additional tools and solutions.
7. Limited Reporting Capabilities
Many traditional GRC software solutions have limited reporting capabilities, making it difficult to generate comprehensive reports that cover all aspects of governance, risk, and compliance. This can make it challenging to provide stakeholders with a clear picture of the organization’s risk posture.
Why choose Our GRC Software?
When it comes to selecting GRC software for your organization, here are some compelling reasons why our solution stands out:
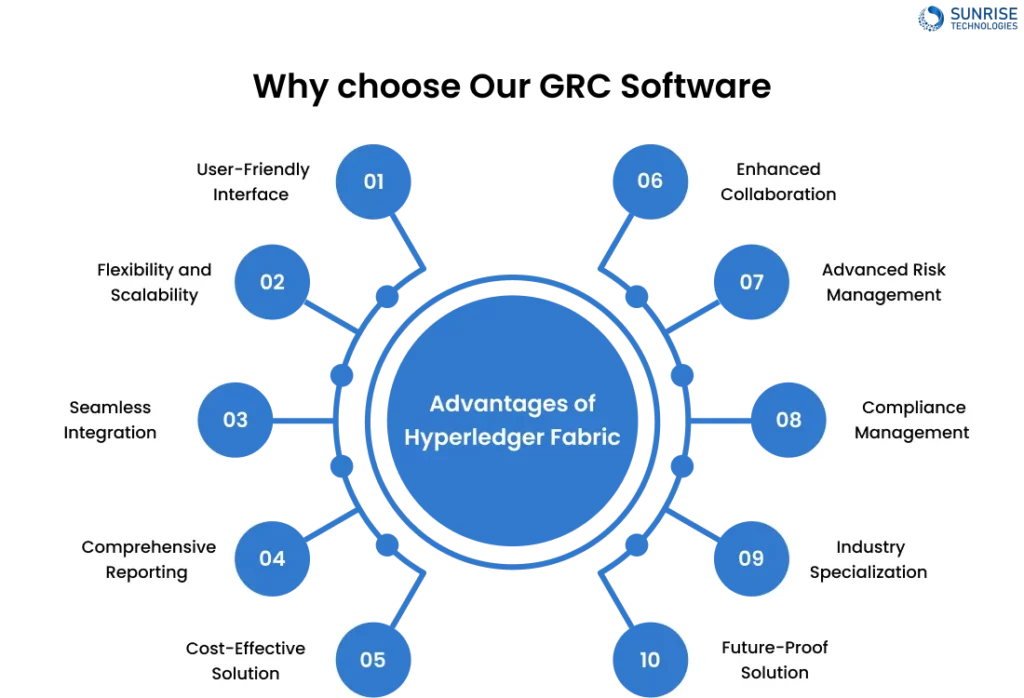
1. User-Friendly Interface
While traditional GRC software has been around for years, it often comes with its own set of challenges that organizations need to be aware of. Here are some of the main issues that companies face when using traditional GRC software:
2. Flexibility and Scalability
Governance risk and compliance software are designed to grow with your organization, offering flexibility and scalability to adapt to changing business needs as you expand and evolve.
3. Seamless Integration
Our GRC software seamlessly integrates with other systems, ensuring data consistency and streamlining processes to provide a comprehensive view of your risk and compliance landscape.
4. Comprehensive Reporting
With robust reporting capabilities, the best GRC software enables you to generate comprehensive reports that cover all aspects of governance, risk, and compliance, giving stakeholders a unified view of your organization’s risk posture.
5. Cost-Effective Solution
GRC software solutions offers a cost-effective solution with reasonable upfront costs and ongoing maintenance fees, making it accessible for organizations of all sizes.
6. Enhanced Collaboration
Our software promotes collaboration and communication among stakeholders, facilitating information sharing, task assignment, and progress tracking on GRC initiatives.
7. Advanced Risk Management
GRC management software provides advanced risk management features, including risk assessments, mitigation plans, and monitoring tools to help you identify, assess, and manage risks effectively.
8. Compliance Management
Financial compliance software simplifies compliance management by tracking regulatory requirements, managing tasks, and generating reports to ensure adherence to relevant laws and standards.
9. Industry Specialization
Our GRC software caters to specific industries, offering tailored solutions that meet the unique needs of your sector while providing the flexibility to adapt outside your specialization.
10. Future-Proof Solution
By choosing our GRC software, you are investing in a future-proof solution that can evolve with your organization, keeping pace with regulatory changes and internal process updates to ensure long-term success.
With the best GRC software, you can streamline your GRC processes, improve risk management, and enhance compliance efforts, setting your organization up for sustainable growth and success.
Not sure which GRC tool suits your business needs? Talk to our experts and get recommendations based on your size, sector, and risk exposure.

Integrating GRC Software into Operations
To implement a robust GRC strategy effectively, organizations can follow these steps:
1. Define GRC Requirements
Understand the organization’s risks and prioritize GRC efforts. Evaluate current risk management and compliance activities, consult with leadership, and align policies with GRC goals. Consider critical business areas and regulatory needs to establish clear objectives.
2. Select Appropriate GRC Software
Identify GRC tools that align with the organization’s needs and address security and compliance gaps. Choose a comprehensive solution that meets all GRC requirements, focusing on automation and unified data management to simplify processes.
3. Prepare for Software Integration
Integrate the chosen GRC software with existing policies and procedures. Seek guidance from the software provider, assign internal roles for implementation, and outline steps for software utilization within the organization.
4. Develop GRC Policies and Procedures
Create detailed GRC policies that align with objectives and regulations. Define roles, risk assessment protocols, and compliance measures. Communicate these policies effectively across the organization to ensure understanding and compliance.
5. Provide Training and Education
Implement training programs to educate employees on GRC concepts and policies. Offer specialized training for staff involved in GRC activities, emphasizing risk awareness, ethical conduct, and necessary skills. Regularly assess the effectiveness of training initiatives.
6. Establish Communication Channels
Integrate the chosen GRC software with existing policies and procedures. Seek guidance from the software provider, assign internal roles for implementation, and outline steps for soft Create open channels for reporting risks, compliance issues, and ethical concerns. Encourage feedback to enhance GRC processes. Implement confidential reporting systems like whistleblower hotlines to promote transparency and accountability. ware utilization within the organization.
7. Conduct Internal Audits and Assessments
Regularly perform internal audits to evaluate GRC effectiveness. Review controls, assess compliance levels, and identify areas for enhancement. Document findings and develop action plans for improvement.
8. Monitor GRC Progress
Continuously track GRC implementation, assess performance against set metrics, review controls, and update policies as needed. Stay informed about regulatory changes and industry standards to maintain effective risk management and compliance.
9. Drive Continuous Improvement
Cultivate a culture of ongoing improvement in GRC practices. Encourage feedback, conduct regular reviews, stay abreast of emerging risks and regulations, and benchmark against industry peers to enhance GRC processes continually.
10. Establish a GRC Committee
Form a dedicated GRC committee with representatives from various departments to provide oversight and guidance. Regularly review performance, address challenges, and make strategic decisions to strengthen the overall GRC framework and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
How can custom GRC software help Australian builders avoid compliance fines?
In high-risk industries like construction, especially in Australia where regulatory frameworks such as WHS, NCC, and ISO 45001 are strictly enforced, failing to stay compliant can lead to hefty penalties, project delays, or even business shutdowns. While generic GRC software provides a foundation, custom-built compliance software can address industry-specific challenges and legal obligations faced by Australian builders.
Here’s how:
- Tailored Compliance Workflows – Custom software ensures that all local, state, and federal construction regulations are integrated into your daily operations, reducing the risk of oversight.
- Real-Time Reporting & Audit Trails – Get automated alerts, documentation logs, and incident reporting tools that keep you audit-ready.
- Site-Specific Safety Checks – Incorporate tools for daily safety assessments, equipment checks, and worker certifications unique to your sites.
- Integration with Industry Systems – Sync data with project management tools, payroll systems, and HR software to ensure nothing falls through the cracks.
Custom GRC software acts as a proactive shield—not just preventing fines, but building a culture of accountability and operational excellence.
Investing in GRC software is a strategic decision that can drive operational excellence, mitigate risks, and foster sustainable growth for organizations across various industries. By harnessing the power of GRC software, businesses can navigate complex regulatory environments, optimize financial processes, and achieve long-term success in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Sam is a chartered professional engineer with over 15 years of extensive experience in the software technology space. Over the years, Sam has held the position of Chief Technology Consultant for tech companies both in Australia and abroad before establishing his own software consulting firm in Sydney, Australia. In his current role, he manages a large team of developers and engineers across Australia and internationally, dedicated to delivering the best in software technology.

Cloud Based Project Management Platform
Read the challenges we faced and how we helped
View Case Study